[OS] Process - Operation in Processes
27 Apr 2020
Process Creation
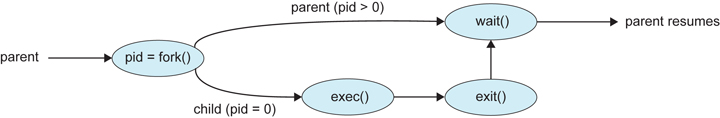
Process (parent) creates new process (child)
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == -1) {
perror("fork failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else if (pid == 0) {
printf("Hello from the child process!\n");
_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else {
int status;
(void)waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
This is a sample code for create child process and waits for it to terminate.
First, parent calls for fork() system call and gets pid.
with fork() call, child gets the copy of exactly same segment with parent. That is, program counter has same point with parent.
if pid is 0, this is child process. if pid > 0, this is parent process. (if pid == -1, fork failed)
in child process, it prints message and terminates with exit() call.
in parent process, it waits its child to be terminated with waitpid() call.
Process Termination
When process finished its job, it calls exit() system call and request OS to remove its all resources.
On the other hand, process can be terminated with some system calls from another process. Those process who send kill signal must have a privilege for that.
Kernel might kill some process in certain circumstances like resource starvation.
References
- https://www.cs.uic.edu/~jbell/CourseNotes/OperatingSystems/3_Processes.html
- https://yongho1037.tistory.com/563
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fork_(system_call)
- https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%ED%8F%AC%ED%81%AC_(%EC%8B%9C%EC%8A%A4%ED%85%9C_%ED%98%B8%EC%B6%9C)
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/726690/what-killed-my-process-and-why